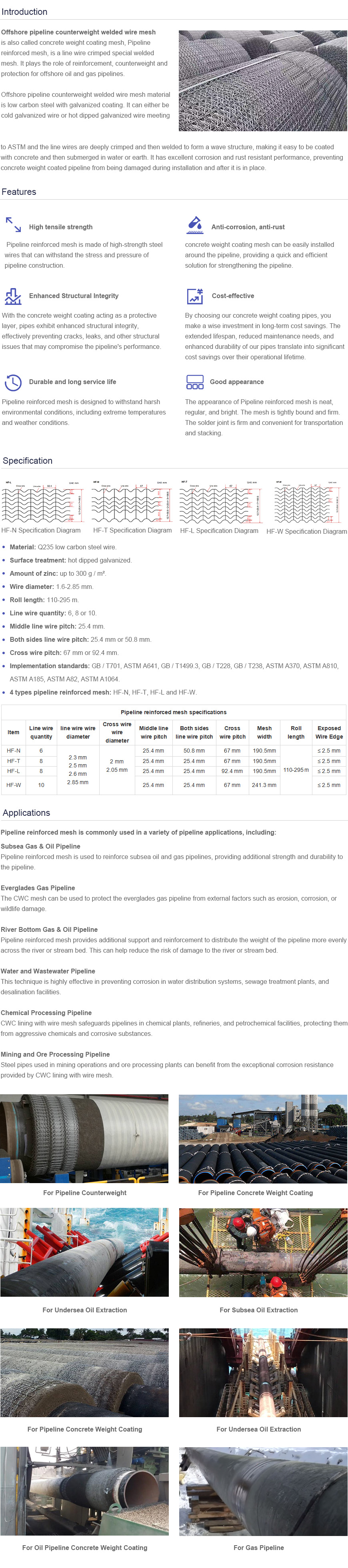
- Industrial zone, South of Anping Town, Hengshui, Hebei, China.
- sales@hfpetromesh.com
- +86-18931809706
Steel Grating Thickness Specifications | Durable & Reliable Solutions
Understanding Steel Grating Thickness A Key Factor in Structural Integrity
Steel grating is an essential material used in various industrial, commercial, and architectural applications. Its versatility and strength make it an ideal choice for constructing walkways, platforms, and stair treads. One crucial aspect of steel grating that significantly influences its performance and longevity is its thickness. Understanding this factor is vital for engineers, architects, and project managers involved in the design and construction of steel structures.
What is Steel Grating?
Steel grating is a flat product made by welding or integrating bars or plates in a specific pattern. The openings in the grating allow for light, air, and water to pass through, making it suitable for environments like factories, parking structures, and outdoor spaces. The applications range from flooring to drainage covers and safety barriers.
Importance of Thickness
The thickness of steel grating, typically measured in millimeters or inches, plays a critical role in its load-bearing capacity and overall durability. Thicker grating can support more weight and withstand more significant impacts, making it vital in settings where heavy equipment and foot traffic occur. For example, a thicker grating is often used in loading docks or industrial warehouses, where heavy machinery operates regularly.
Factors Influencing Grating Thickness
steel grating thickness
Several factors determine the required thickness of steel grating in a given application
1. Load Requirements The anticipated load is the primary consideration for thickness. Engineers often refer to load tables, which specify the maximum loads that various thicknesses can handle. These tables account for static loads (like the weight of workers and equipment) and dynamic loads (such as moving vehicles).
2. Span Length The distance between support beams affects the choice of thickness. Longer spans require thicker grating to prevent sagging and ensure safety. For example, a grating spanning eight feet would typically require a greater thickness than one spanning just four feet.
3. Environmental Conditions The setting in which the grating will be installed also impacts thickness. Environments subject to corrosive agents, such as saltwater or chemicals, require thicker grating to ensure a longer lifespan. Additional protective coatings may also be factored into the design.
4. Safety Regulations Compliance with local building codes and safety regulations is another critical factor. These regulations often specify minimum thickness standards based on the application, particularly in public areas where safety is paramount.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate thickness of steel grating is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity and safety of a project. By considering factors such as load requirements, span lengths, environmental conditions, and safety regulations, engineers and designers can make informed decisions. Ultimately, the right thickness not only guarantees safety and performance but also contributes to the longevity of the structure. As the construction industry evolves, understanding the nuances of steel grating, including thickness, will remain a fundamental aspect of successful design and planning.
-
The Power of Pyramid Shaker Screen - A 3-Dimensional SolutionNewsOct.24,2024
-
Exploring the Versatility and Durability of Steel GratingNewsOct.24,2024
-
Revolutionizing Drilling Efficiency with Steel Frame Shaker Screens for Mud Shale ShakersNewsOct.24,2024
-
Potential of Shale Shaker ScreensNewsOct.24,2024
-
Offshore Pipeline Counterweight Welded Mesh - Reinforced Mesh in Marine EngineeringNewsOct.24,2024
-
Revolutionizing Offshore Pipeline Stability with Concrete Weight Coating MeshNewsOct.24,2024
