- Industrial zone, South of Anping Town, Hengshui, Hebei, China.
- sales@hfpetromesh.com
- +86-18931809706
2 月 . 01, 2025 03:39
Back to list
serrated steel grating
Serrated grating weight is an aspect that often goes unnoticed when selecting the ideal material for industrial and commercial applications, yet it plays a crucial role in both performance and safety. With decades of industrial expertise, understanding the unique qualities of serrated grating weight can provide an edge in decision-making, ensuring that projects meet both functional and safety standards while optimizing costs.
Fiberglass serrated grating stands out due to its exceptionally lightweight and non-corrosive properties. It's often the go-to for chemical plants or aquatic applications where metal gratings would fail due to rust or chemical reaction. While its lightweight nature facilitates easy installation and reduces transportation costs, it is important to note that fiberglass may not offer the same load-bearing capacity as metal options. However, in environments where safety from electric conductivity is a concern, fiberglass is unmatched. When evaluating serrated grating for a project, it is crucial to consider the weight in relation to its application. Load rating, environmental conditions, and maintenance needs are all factors that must be assessed. A thorough understanding of these aspects enhances the credibility and trustworthiness in advising and selecting the most fitting serrated grating type. The expertise involved in selecting the proper serrated grating also extends to compliance with safety standards. Ensuring that the weight of the grating aligns with industry regulations is not just a matter of legal adherence but also of safeguarding lives and infrastructure. Consulting with engineers and safety experts during the planning phase can greatly enhance the author's expertise and authoritativeness in this field, reinforcing trust from stakeholders. Overall, the weight of serrated grating is a pivotal element in the selection process that demands careful balance. It requires an in-depth understanding of material science, structural engineering, and environmental challenges. By coupling these insights with real-world experiences and expert evaluations, decision-makers can confidently select serrated grating that optimizes performance, safety, and cost-efficiency for any application.
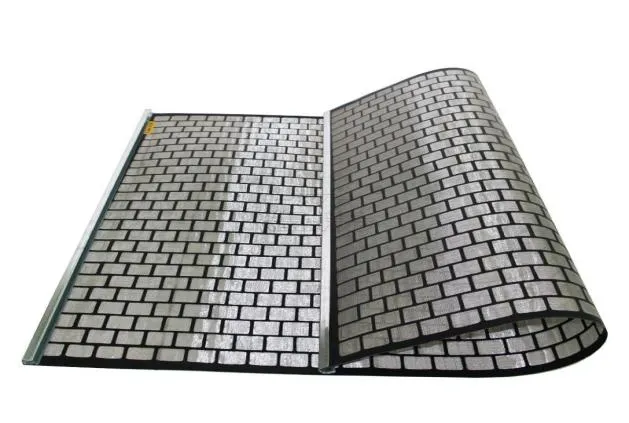
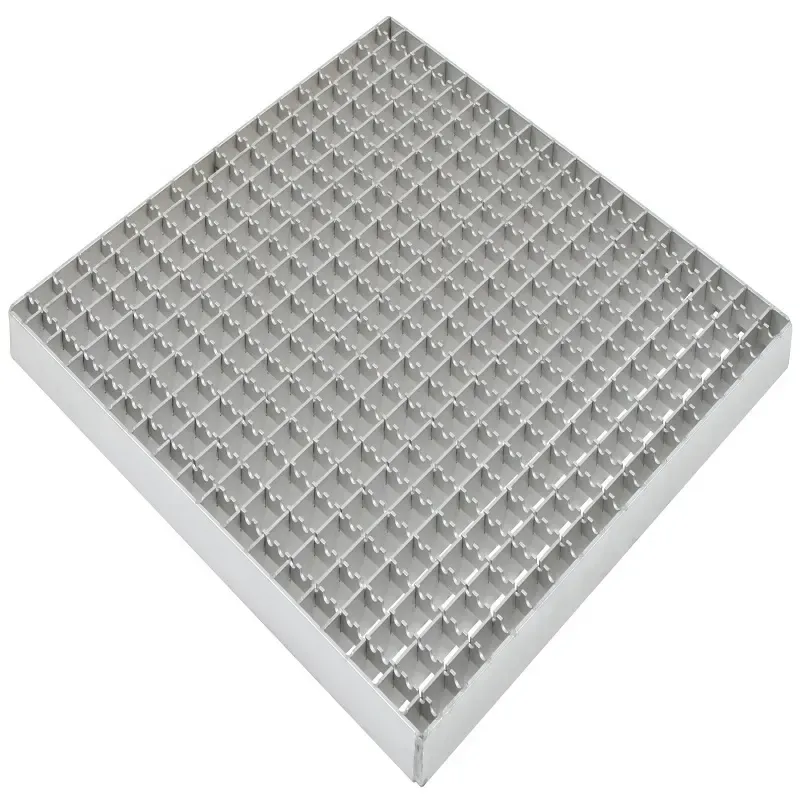

Fiberglass serrated grating stands out due to its exceptionally lightweight and non-corrosive properties. It's often the go-to for chemical plants or aquatic applications where metal gratings would fail due to rust or chemical reaction. While its lightweight nature facilitates easy installation and reduces transportation costs, it is important to note that fiberglass may not offer the same load-bearing capacity as metal options. However, in environments where safety from electric conductivity is a concern, fiberglass is unmatched. When evaluating serrated grating for a project, it is crucial to consider the weight in relation to its application. Load rating, environmental conditions, and maintenance needs are all factors that must be assessed. A thorough understanding of these aspects enhances the credibility and trustworthiness in advising and selecting the most fitting serrated grating type. The expertise involved in selecting the proper serrated grating also extends to compliance with safety standards. Ensuring that the weight of the grating aligns with industry regulations is not just a matter of legal adherence but also of safeguarding lives and infrastructure. Consulting with engineers and safety experts during the planning phase can greatly enhance the author's expertise and authoritativeness in this field, reinforcing trust from stakeholders. Overall, the weight of serrated grating is a pivotal element in the selection process that demands careful balance. It requires an in-depth understanding of material science, structural engineering, and environmental challenges. By coupling these insights with real-world experiences and expert evaluations, decision-makers can confidently select serrated grating that optimizes performance, safety, and cost-efficiency for any application.
Share
Prev:
Next:
Latest news
-
The Power of Pyramid Shaker Screen - A 3-Dimensional SolutionNewsOct.24,2024
-
Exploring the Versatility and Durability of Steel GratingNewsOct.24,2024
-
Revolutionizing Drilling Efficiency with Steel Frame Shaker Screens for Mud Shale ShakersNewsOct.24,2024
-
Potential of Shale Shaker ScreensNewsOct.24,2024
-
Offshore Pipeline Counterweight Welded Mesh - Reinforced Mesh in Marine EngineeringNewsOct.24,2024
-
Revolutionizing Offshore Pipeline Stability with Concrete Weight Coating MeshNewsOct.24,2024
