- Industrial zone, South of Anping Town, Hengshui, Hebei, China.
- sales@hfpetromesh.com
- +86-18931809706
1 月 . 26, 2025 03:58
Back to list
aluminum bar grating weight
Aluminum bar grating stands as an indispensable solution in various industrial and architectural applications. Its popularity stems from its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it a prime choice where both durability and lightweight properties are paramount. When calculating the weight of aluminum bar grating, several factors come into play, influencing both performance and installation. A deeper understanding of these aspects not only assists in precise weight estimation but also optimizes structural planning and efficiency.
Surface treatment of the aluminum grating is another pivotal factor. While untreated grating offers the lowest weight, powder coating or anodizing provides additional corrosion resistance at a marginal weight increase. Such coatings are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of the grating in corrosive environments, justifying the slight addition in weight. Understanding these variables aids in calculating the precise weight of aluminum bar grating for any given project. When undertaking structural planning, it’s advisable to consult with suppliers and use weight calculators that account for all design specifications. Doing so ensures that the chosen grating not only fulfills the functional requirements but also aligns with logistical preferences, such as transportation and installation ease. Ultimately, the lightweight attributes of aluminum bar grating offer ample opportunities for innovation across industries. Its ability to maintain structural integrity while reducing overall weight translates into significant cost savings during both construction and lifetime maintenance. Moreover, leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques and materials science continues to improve the efficacy and sustainability of these solutions, reinforcing aluminum bar grating as a top contender in modern engineering projects. As advancements in material technology evolve, aluminum bar grating remains a versatile and adaptable solution, ideal for a myriad of applications where weight efficiency, strength, and durability are non-negotiable.
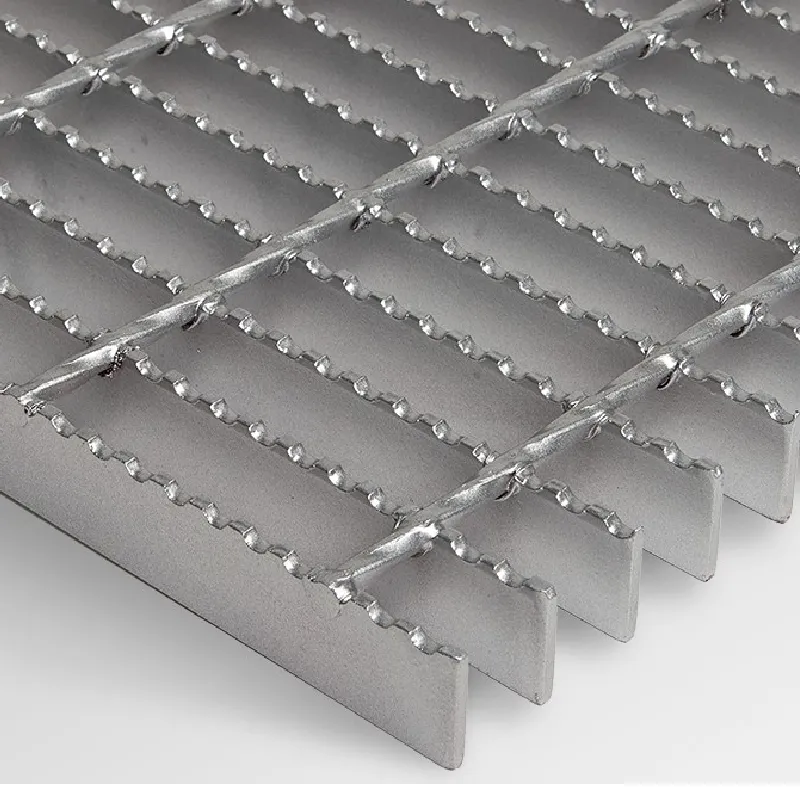

Surface treatment of the aluminum grating is another pivotal factor. While untreated grating offers the lowest weight, powder coating or anodizing provides additional corrosion resistance at a marginal weight increase. Such coatings are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of the grating in corrosive environments, justifying the slight addition in weight. Understanding these variables aids in calculating the precise weight of aluminum bar grating for any given project. When undertaking structural planning, it’s advisable to consult with suppliers and use weight calculators that account for all design specifications. Doing so ensures that the chosen grating not only fulfills the functional requirements but also aligns with logistical preferences, such as transportation and installation ease. Ultimately, the lightweight attributes of aluminum bar grating offer ample opportunities for innovation across industries. Its ability to maintain structural integrity while reducing overall weight translates into significant cost savings during both construction and lifetime maintenance. Moreover, leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques and materials science continues to improve the efficacy and sustainability of these solutions, reinforcing aluminum bar grating as a top contender in modern engineering projects. As advancements in material technology evolve, aluminum bar grating remains a versatile and adaptable solution, ideal for a myriad of applications where weight efficiency, strength, and durability are non-negotiable.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
The Power of Pyramid Shaker Screen - A 3-Dimensional SolutionNewsOct.24,2024
-
Exploring the Versatility and Durability of Steel GratingNewsOct.24,2024
-
Revolutionizing Drilling Efficiency with Steel Frame Shaker Screens for Mud Shale ShakersNewsOct.24,2024
-
Potential of Shale Shaker ScreensNewsOct.24,2024
-
Offshore Pipeline Counterweight Welded Mesh - Reinforced Mesh in Marine EngineeringNewsOct.24,2024
-
Revolutionizing Offshore Pipeline Stability with Concrete Weight Coating MeshNewsOct.24,2024
